The Spanish Dehesa, An Ecosystem Rich In Biodiversity

Spain is distinguished by a great variety of landscapes and ecosystems. Within this great variety, the Dehesa is one of the ecosystems that presents the greatest biodiversity thanks to its enormous agroforestry resources.
What is the Dehesa?
It is an ecosystem that we can somehow define as “artificial”. It is the result of the transformation of the Mediterranean forest into pasture. It is made up of holm oak and cork woods used for grazing animals. It is located in the southwestern side of the Iberian Peninsula, particularly in the regions of Castile and León, Extremadura and Andalusia.
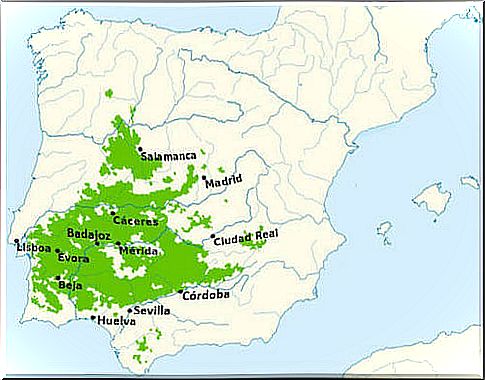
La Dehesa is considered a system of high naturalistic value and the greatest example in Spain of an agrosilvopastoral use of a territory.
The importance of the Dehesa in Spain
The importance of any agricultural ecosystem is evaluated from different perspectives with the aim of exploiting it in the best possible way.
Agricultural importance
The richness of the Dehesa ecosystem does not lie exactly in its agricultural vocation. The soils are poor, even if their quality allows to graze many species of livestock.
The resources present in the Dehesa have been used for centuries for the extensive breeding of livestock. The holm oak, in fact, is used as a food resource for animals, both in its natural form and in the form of forage. Furthermore, in these territories the “montanera” regime is used to feed the Iberian pig from which the famous “jamón de belota” is obtained.
In these territories, the shrub layer is the one that has been most affected by the action of man. In an effort to maximize grazing areas, this layer of vegetation has been minimized or almost disappeared. This practice is known in Spain as “limpiar la dehesa” (cleaning the pasture).
Importance of livestock
In the Spanish Dehesa we can find all kinds of livestock. Among them are:
- Sheep. The merino sheep breed is the most represented. However, there are also breeds such as the “Manchega” or the “Castellana”.

- The Iberian black pig. It is the best known and most emblematic species.
- Cattle. Generally, native breeds of beef cattle such as the “Avileña” or the “Morucha”. In addition, the breed of Toro bravo de Lidia is presented.

- Goats (little represented).
- Occasionally, there is the presence of the Spanish horse (the Andalusian) and the Spanish donkey.
Economic and social importance of the Dehesa
La Dehesa is an ecosystem made up of vast areas of territory that host numerous activities in the agri-food sector. It is, therefore, a source of employment for a high percentage of the Spanish population.
However, they are territories that have a limited capacity for economic development because they do not have sufficiently competitive industries.
Maintaining grazing areas would be very important to avoid excessive migration from the countryside to the cities and to avoid the phenomenon known in Spain as “empty Spain” (phenomenon of rural abandonment). In this sense, numerous action plans have been developed which include measures such as:
- Improving the use of environmental, agricultural and livestock resources.
- The inclusion of Dehesa in the action plans for circular economy.
Why can the Dehesa be a source of wealth?
The abandonment of large-scale livestock farms is causing dramatic consequences. For example, the aging of populations in rural areas, the increase in the mortality rate and the reduction of economic activities.
To attract people to these territories, it is essential to make them attractive, especially to young people. One way could be the enhancement of rural gastronomic tourism, thanks to which an emotional bond can be developed with the environment that is difficult to break.
For this reason, the focus was on the production of the so-called “Dehesa products”. Some of them have obtained the protected designation of origin (PDO) or the protected geographical indication (PGI). One example is the famous Iberian ham (jamón iberico or pata negra).









